Put Options Explained: A Complete Guide to Trading and Strategy
A put option is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not obligation, to sell an asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specific timeframe. This tool is commonly used for hedging against market downturns or speculating on falling prices.
Key Features of Put Options:
- Strike Price: The guaranteed selling price
- Expiration Date: Deadline to exercise the option
- Premium: Cost paid to purchase the option
- Intrinsic Value: Difference between strike price and market price

Hand pressing digital trading button
How Put Options Work:
- Value increases as underlying asset price decreases
- Commonly used for portfolio protection
- Can be traded through specialized brokers
- Time decay reduces option value as expiration approaches
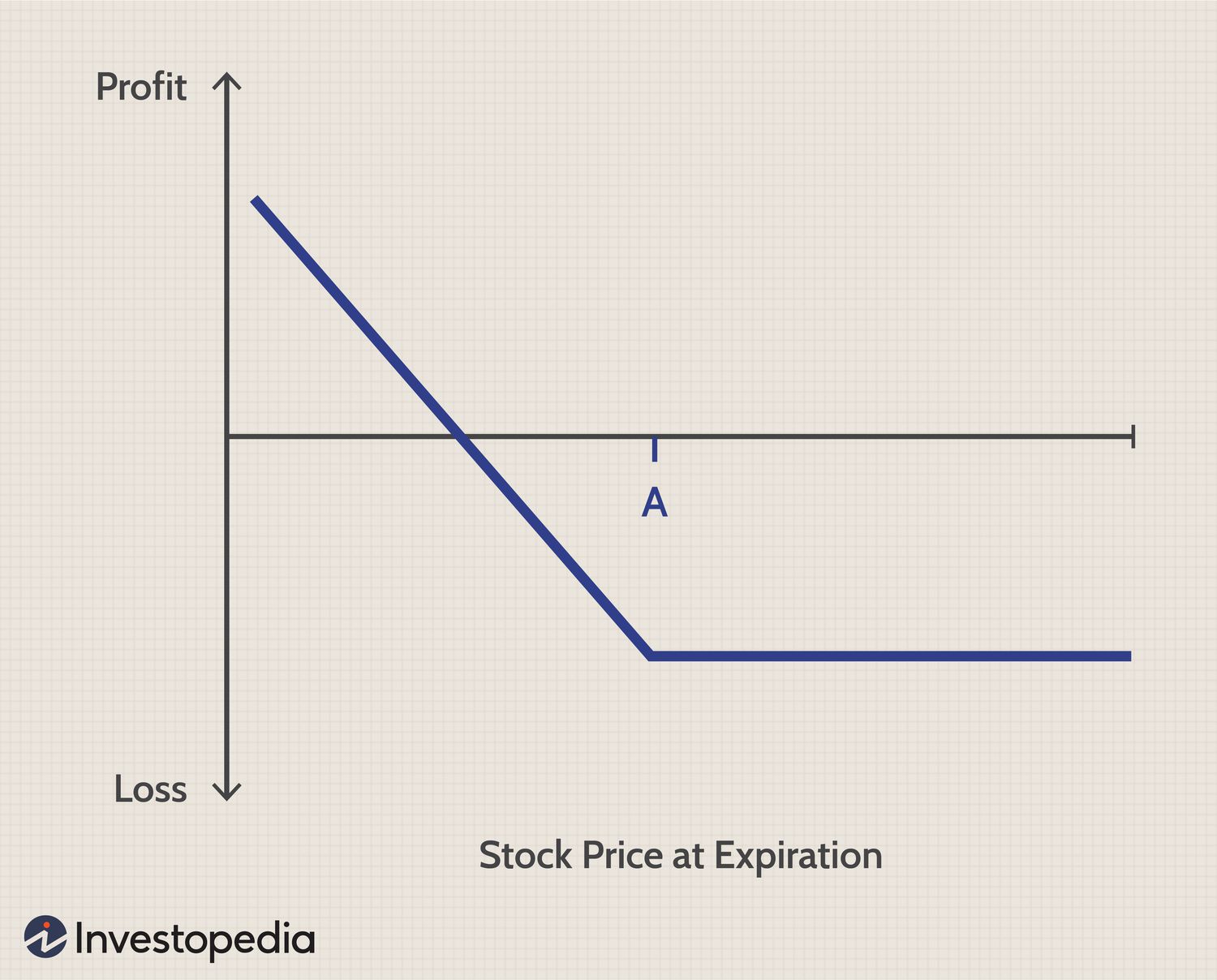
Put option price chart graph
Example: If you buy a put option with a $50 strike price when a stock trades at $50, and the stock falls to $40, you can:
- Exercise the option to sell at $50
- Sell the option for a profit
- Let it expire if the stock price rises above $50
Risk Considerations:
- Maximum loss limited to premium paid (for buyers)
- Maximum profit is strike price minus premium (if stock goes to zero)
- Time decay works against option buyers
- Writing puts carries potentially significant risk
Trading Strategy: Most traders sell valuable options rather than exercise them because:
- Captures remaining time value
- Reduces transaction costs
- Avoids additional margin requirements
- Provides more immediate liquidity
Put options are essential tools for risk management and speculative trading, but require careful consideration of market conditions, timing, and risk tolerance.
Related Articles
ETF Guide: Understanding Exchange-Traded Funds for Smart Investing

